Introduction
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) have become essential tools for optimizing logistics and inventory management, particularly in an environment where efficiency is critical. Organizations aiming to enhance their operational capabilities must understand the best practices for implementing these advanced systems.
Businesses face various challenges when integrating a WMS, including:
- Resistance to change
- Data migration issues
- The need for employee training
Navigating these complexities is vital to fully realize the potential of their investment.
This article explores essential strategies for successful WMS implementation. By focusing on these insights, organizations can achieve increased efficiency, improved accuracy, and ultimately, greater customer satisfaction.
Define Warehouse Management Systems and Their Core Functions
A Storage Management System (WMS) is a sophisticated software solution that utilizes WMS solutions to optimize and manage storage operations effectively. Its core functions encompass several critical areas:
-
Inventory Management: WMS tracks inventory levels, locations, and movements in real-time. This ensures accurate stock counts and significantly reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking. This capability is crucial as the worldwide warehouse operations market is expected to increase from USD 2.88 billion in 2024 to USD 3.38 billion in 2025. As Indy Pereira observes, "The key factor that is propelling the WMS market expansion includes evolving supply chain models of product manufacturers and swiftly rising consumer demand," emphasizing the growing dependence on efficient inventory control solutions.
-
Order Fulfillment: The system streamlines the picking, packing, and shipping processes, enhancing order accuracy and speed. Modern WMS solutions now incorporate features such as waveless picking and dynamic order release, which were previously exclusive to WES. This evolution allows businesses to respond more swiftly to customer demands.
-
Receiving and Putaway: WMS manages the inbound logistics process, ensuring that goods are received, inspected, and stored efficiently. This function is crucial for maintaining operational flow and minimizing delays in inventory availability.
-
Labor Management: By monitoring workforce productivity and effectively allocating tasks, WMS optimizes labor costs and improves overall efficiency. The labor market is unpredictable due to swift alterations in federal funding, immigration regulations, tariffs, and other governmental policies that could impact businesses. Thus, efficient labor oversight is increasingly essential.
-
Reporting and Analytics: WMS offers valuable insights into storage facility performance through comprehensive data analysis. This functionality enables organizations to make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and adapt to changing market conditions.
Experts emphasize that effective inventory management with WMS solutions is not just about tracking stock; it is about creating a responsive and agile supply chain. As the logistics landscape evolves, integrating advanced technologies such as AI and automation into WMS will further enhance these core functions, driving efficiency and improving customer satisfaction.

Highlight Key Benefits of Implementing a WMS
Implementing a Warehouse Management System (WMS) offers numerous advantages that can significantly enhance logistics operations.
-
Increased Efficiency: Automation of warehouse processes greatly reduces manual errors and speeds up operations. Companies that have adopted WMS solutions report a 50-200% increase in warehouse throughput, emphasizing the potential for faster order fulfillment. For example, Exist, an e-commerce retailer, boosted its outbound deliveries from 10,000 to nearly 60,000 per day within just three months of implementing a WMS.
-
Improved Inventory Accuracy: Real-time tracking capabilities help minimize discrepancies, ensuring that inventory levels remain consistently accurate. Businesses utilizing WMS have achieved inventory accuracy rates of 99.9% or higher. The E-3PL platform exemplifies this success, achieving such an order accuracy rate and demonstrating the effectiveness of WMS in enhancing inventory management.
-
Cost Reduction: By optimizing labor and minimizing waste, organizations can significantly lower operational costs. Companies implementing WMS have reported reductions in holding costs by over 20% and operational costs by up to 25%, showcasing the financial benefits of these systems.
-
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Faster and more accurate order processing directly contributes to improved customer experiences and loyalty. With WMS, businesses can ensure timely deliveries and accurate order fulfillment, leading to higher customer satisfaction levels, with picking accuracy also reaching 99.9%.
-
Scalability: A WMS is designed to grow alongside the business, adapting to increased inventory and order volumes without compromising performance. This flexibility is crucial as e-commerce sales are projected to rise significantly, necessitating robust logistics solutions to meet growing demand.

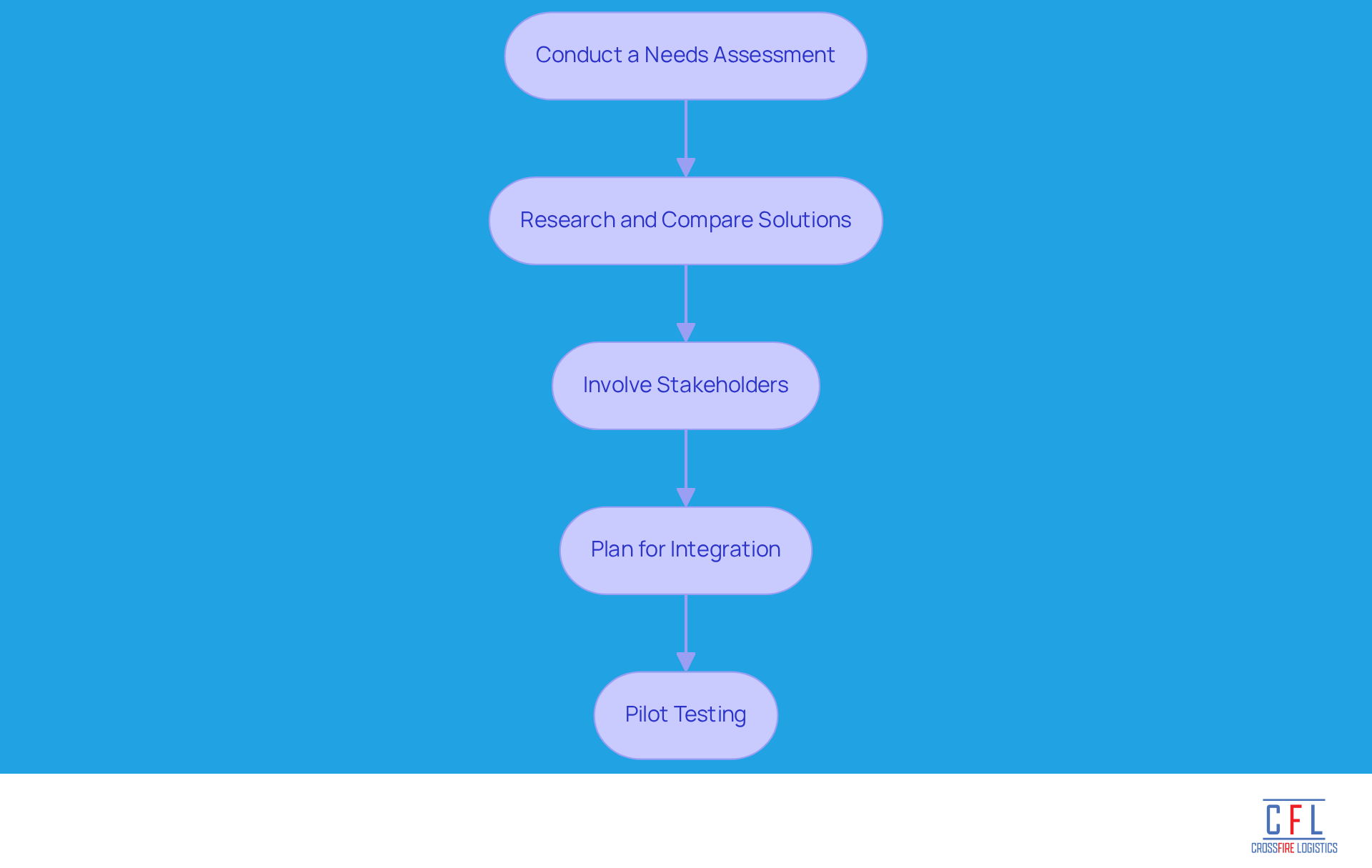
Outline Best Practices for Selecting and Implementing WMS Solutions
To effectively select and implement a Warehouse Management System (WMS), organizations should adhere to the following best practices:
-
Conduct a Needs Assessment: Begin by thoroughly evaluating current storage operations to pinpoint specific needs and challenges that a WMS can effectively address. This step is essential, as 44% of storage software purchasers prioritize order processing features, emphasizing the demand for customized solutions.
-
Research and Compare Solutions: Investigate various WMS options, focusing on essential features, scalability, and vendor support. With 80% of organizations in warehousing planning to invest in new technologies, understanding the landscape of available solutions is vital for making informed decisions. The worldwide market for WMS solutions is anticipated to attain USD 3.38 billion in 2025, indicating the increasing significance of warehouse management systems in the logistics industry.
-
Involve Stakeholders: Engage key stakeholders from various departments to gather diverse input and ensure the chosen solution meets the varied needs of the organization. This collaborative approach can enhance buy-in and facilitate smoother implementation.
-
Plan for Integration: Ensure that the WMS can seamlessly connect with existing platforms, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Transportation Management Solutions (TMS), to facilitate efficient data flow. A well-integrated system can significantly improve operational efficiency and reduce errors.
-
Pilot Testing: Conduct pilot tests to identify potential issues and gather user feedback before full-scale implementation. This step allows organizations to refine their processes and ensure that the WMS aligns with operational goals, ultimately leading to a smoother transition.
By adhering to these best practices, organizations can increase their likelihood of successful WMS solutions implementation, driving efficiency and enhancing overall storage management. Notably, 83% of warehousing and logistics providers used a WMS in 2021, down from 93% in 2018, indicating a need for effective implementation strategies. Moreover, 77% of respondents concur on the need to update their storage operations but are sluggish to adopt new technology, emphasizing typical obstacles encountered during WMS implementation. The analytics and optimization segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 22.3% from 2025 to 2030, underscoring the importance of data-driven decision-making in warehouse operations.
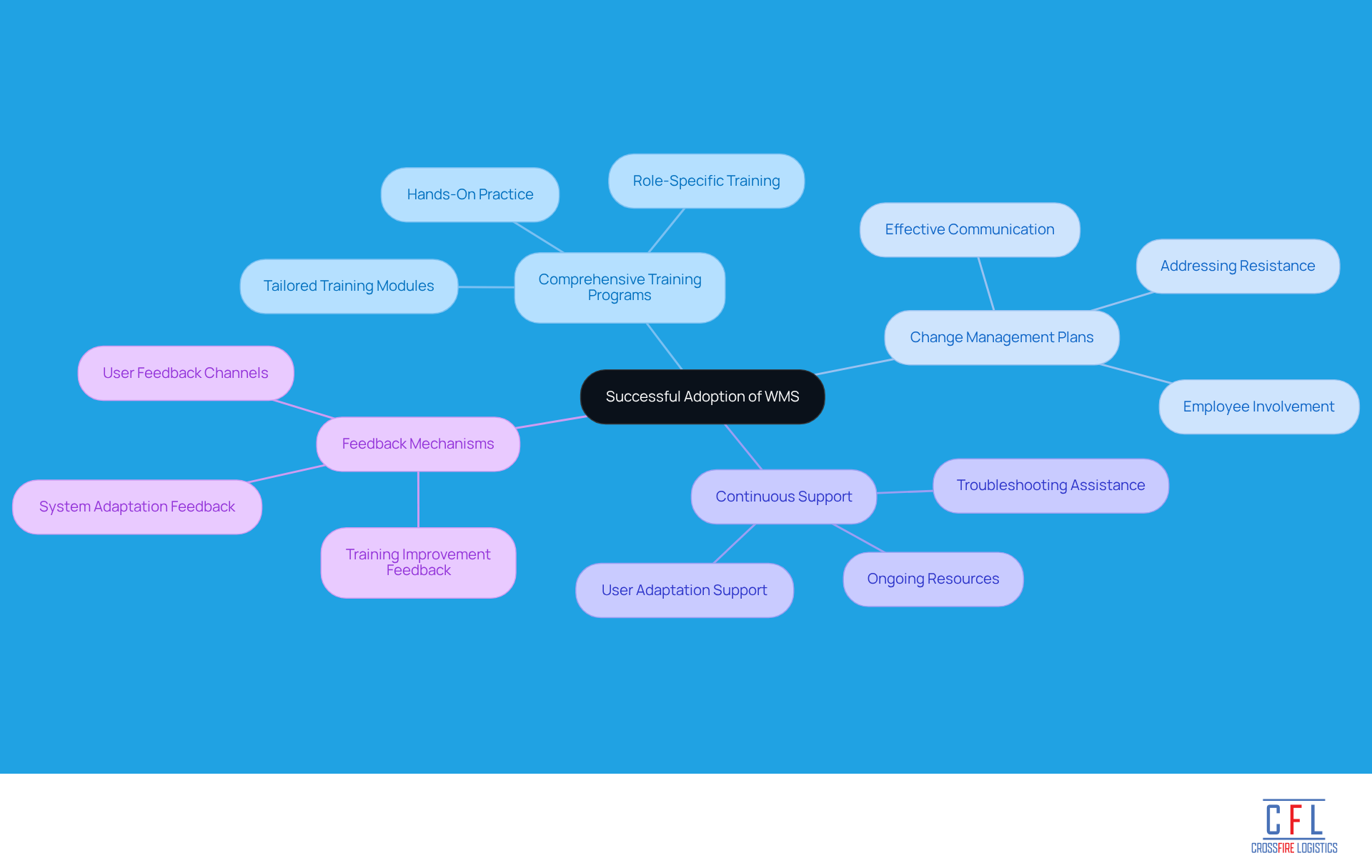
Emphasize Training and Change Management Strategies for Successful Adoption
To ensure successful adoption of a Warehouse Management System (WMS), organizations should focus on several key areas:
-
Comprehensive Training Programs: It is essential to develop training modules that encompass all aspects of the WMS. These modules should be tailored to different user roles, enhancing understanding and proficiency among all users.
-
Change Management Plans: A structured change management strategy is crucial. This plan should address potential resistance, effectively communicate the advantages of the new framework, and actively involve employees in the transition process.
-
Continuous Support: Providing ongoing support and resources after implementation is vital. This support helps users adapt to the new system and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
-
Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing channels for users to provide feedback on both the system and the training is important. This allows for continuous improvement and adaptation, ensuring the WMS meets the evolving needs of the organization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, implementing an effective Warehouse Management System (WMS) is essential for organizations aiming to improve their logistics operations and meet the changing demands of the marketplace. Understanding the core functions of WMS - such as inventory management, order fulfillment, and labor management - enables businesses to optimize their storage processes and enhance efficiency.
This article has outlined several best practices for selecting and implementing WMS solutions. Key steps include:
- Conducting a thorough needs assessment
- Involving key stakeholders
- Planning for seamless integration with existing systems
Furthermore, the significance of comprehensive training and structured change management strategies is critical, as these elements are vital for ensuring successful adoption and maximizing the benefits of WMS.
Ultimately, the implementation of a WMS transcends a mere technological upgrade; it represents a strategic initiative that can profoundly influence operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall business growth. Organizations should embrace these best practices, invest in suitable solutions, and prepare their teams for a smooth transition to fully leverage the advantages of advanced warehouse management systems in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a sophisticated software solution designed to optimize and manage storage operations effectively.
What are the core functions of a WMS?
The core functions of a WMS include inventory management, order fulfillment, receiving and putaway, labor management, and reporting and analytics.
How does a WMS assist in inventory management?
A WMS tracks inventory levels, locations, and movements in real-time, ensuring accurate stock counts and reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
What role does a WMS play in order fulfillment?
A WMS streamlines the picking, packing, and shipping processes, enhancing order accuracy and speed, and incorporates advanced features like waveless picking and dynamic order release.
How does a WMS manage receiving and putaway processes?
A WMS oversees the inbound logistics process, ensuring that goods are received, inspected, and stored efficiently, which helps maintain operational flow and minimize delays.
What is the significance of labor management in a WMS?
Labor management in a WMS involves monitoring workforce productivity and allocating tasks effectively, optimizing labor costs, and improving overall efficiency.
How does a WMS provide reporting and analytics?
A WMS offers valuable insights into storage facility performance through comprehensive data analysis, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and enhance operational efficiency.
Why is effective inventory management important in a WMS?
Effective inventory management with WMS solutions is crucial for creating a responsive and agile supply chain, adapting to evolving logistics landscapes.
What advancements are expected to enhance WMS functions in the future?
The integration of advanced technologies such as AI and automation into WMS is expected to further enhance core functions, driving efficiency and improving customer satisfaction.




