Introduction
Freight data analytics is revolutionizing the logistics landscape. It holds the potential to enhance operational efficiency and drive significant cost savings. By harnessing data from various sources, logistics professionals can optimize shipping processes, improve route planning, and identify inefficiencies that hinder performance.
However, as the industry evolves, a challenge persists: how can organizations effectively leverage these analytics? The goal is not only to streamline operations but also to adapt to the ever-changing demands of the market.
Understand Freight Data Analytics Fundamentals
Freight data analytics involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data related to freight transportation. This includes shipment volumes, routes, carriers, and delivery times. For logistics professionals aiming to enhance their operations, understanding these fundamentals is crucial.
Key Components of Freight Analytics:
- Data Sources: Recognizing where data originates is essential. This includes transportation management systems (TMS), warehouse management systems (WMS), and external data feeds.
- Data Categories: It's important to acknowledge the various categories of information, such as historical shipment records, real-time tracking details, and predictive analysis.
- Analytical Techniques: Familiarity with analytical methods is vital. This includes descriptive analysis (what happened), diagnostic analysis (why it happened), and predictive analysis (what is likely to occur).
By grasping these fundamentals, supply chain experts can leverage information more effectively, enhancing efficiency and refining decision-making processes.
Optimize Shipping Processes with Data-Driven Insights
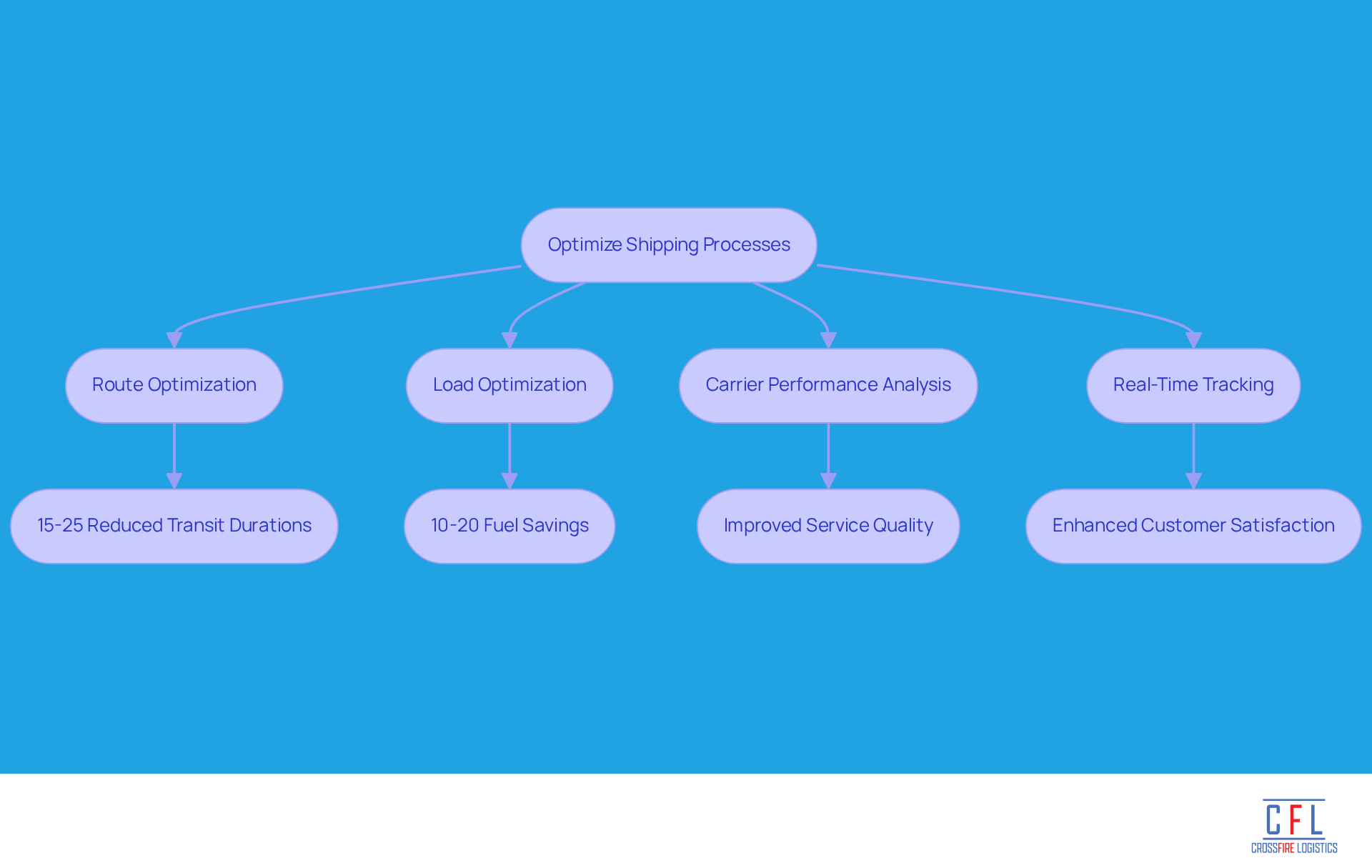
To enhance shipping processes, logistics professionals should adopt data-driven strategies, such as freight data analytics, that streamline operations and improve efficiency.
Route Optimization: By leveraging analytics, companies can identify the most efficient routes through the analysis of historical data, traffic patterns, and delivery windows. AI-driven path planners can reduce transit durations by 15-25% and significantly lower costs, shifting logistics from reactive to proactive operations. Notably, 72% of companies still plan routes manually, leading to inefficiencies that data-driven strategies can effectively address.
Load Optimization: Utilizing shipment information allows businesses to maximize load capacities, ensuring vehicles operate at optimal levels. This strategy not only minimizes the number of trips required but also contributes to fuel savings of 10-20%, aligning with sustainability goals. Companies that implement strategic route optimization often experience similar fuel savings, reinforcing the advantages of these practices.
Carrier Performance Analysis: Employing freight data analytics to assess carrier performance is crucial for identifying the most reliable and cost-effective partners. Key metrics, such as on-time delivery rates and cost per mile, are essential for informed carrier selection, ultimately enhancing overall service quality.
Real-Time Tracking: Implementing real-time tracking systems enables continuous monitoring of shipments, allowing for proactive management of potential delays. This transparency enhances customer satisfaction and facilitates prompt adjustments in planning, ensuring high service levels are maintained.
By integrating these strategies, transportation firms can streamline their shipping operations, reduce costs, and elevate service levels, ultimately driving efficiency and customer satisfaction. It is also vital to establish clear KPIs before implementing these strategies to measure success and avoid misapplication. As Saqib Rehman noted, in supply chain management, speed is important-but control is even more crucial.
Leverage Predictive Analytics for Enhanced Route Planning
Predictive analytics plays a pivotal role in enhancing route planning through several key strategies:
-
Demand Forecasting: Analyzing historical shipping data allows logistics companies to accurately predict future demand patterns. This insight enables optimal resource distribution and informed pathway planning, ensuring that capacity meets anticipated needs.
-
Traffic and Weather Analysis: Real-time information on traffic situations and weather predictions allows transportation companies to flexibly modify pathways. This proactive approach minimizes delays and enhances delivery times, which is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction.
-
Scenario Planning: Running simulations based on various scenarios-such as peak seasons or unexpected road closures-helps identify the most efficient paths and strategies. This foresight prepares logistics teams for potential disruptions, ensuring smoother operations.
-
Performance Metrics: Continuous monitoring of journey performance metrics is essential for refining future planning decisions. By analyzing these metrics, companies can identify areas for improvement and implement changes that enhance efficiency.
-
Information Quality and Integration: The success of predictive analytics significantly depends on the quality and comprehensiveness of information. Ensuring precise and comprehensive information collection through freight data analytics is vital for effective demand forecasting and route optimization. Furthermore, incorporating real-time information streaming improves operational efficiency and delivery security, enabling transport firms to react quickly to shifting circumstances.
-
Common Pitfalls: Logistics coordinators should be aware of common challenges in implementing predictive analysis, such as poor data quality and integration issues. Addressing these pitfalls can prevent misapplication of predictive practices.
Utilizing predictive analysis not only simplifies route planning procedures but also greatly enhances operational efficiency and customer contentment in transportation. Companies that have effectively implemented predictive analytics have reported improvements in on-time delivery rates, showcasing the tangible benefits of these practices.

Identify and Address Inefficiencies through Data Management
To effectively identify and address inefficiencies in logistics operations, companies should prioritize the following data management practices:
-
Data Quality Assessment: Regular audits are essential to ensure data accuracy and completeness. High-quality information is crucial; poor quality can lead to operational inefficiencies and financial losses. Organizations typically lose between 8% and 12% of revenue due to these issues.
-
Centralized Information Systems: Implement centralized information management systems that integrate insights from various sources. This approach provides a comprehensive view of logistics operations, facilitating improved decision-making and minimizing the risk of disjointed information that can hinder performance. In 2025, 57% of supply chain professionals cited insufficient visibility as the biggest challenge facing their operations, highlighting the urgency of this practice.
-
Performance Analytics: Leverage performance analytics to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies within the supply chain. Key metrics, such as order fulfillment times and inventory turnover rates, are vital for pinpointing areas needing improvement, allowing companies to optimize their operations effectively.
-
Ongoing Enhancement: Foster an environment of continuous improvement by regularly assessing information and processes. This proactive approach helps organizations uncover new opportunities for efficiency gains and adapt to changing market demands. Furthermore, 62% of industry leaders recognized labor shortages as a significant challenge, emphasizing the importance of efficient information management practices in addressing workforce limitations.
By concentrating on these information management practices, transport firms can enhance operational performance, reduce expenses, and elevate overall service quality, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction. Understanding how to leverage freight data analytics has become a necessity rather than an option.

Conclusion
Freight data analytics serves as a vital tool in optimizing logistics operations. By grasping the fundamentals of freight analytics, logistics professionals can leverage data to enhance efficiency, refine decision-making, and elevate service quality. Integrating data-driven insights into shipping processes allows companies to shift from reactive to proactive strategies, resulting in substantial cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Key practices such as route optimization, load optimization, and real-time tracking are critical for maximizing operational efficiency. Furthermore, utilizing predictive analytics for demand forecasting, traffic analysis, and scenario planning enables logistics firms to anticipate potential challenges. Addressing inefficiencies through robust data management practices - like data quality assessments and centralized information systems - further boosts performance and mitigates revenue losses.
The importance of freight data analytics is paramount. As the logistics industry evolves, adopting these best practices becomes essential for companies striving to maintain competitiveness. By emphasizing data-driven strategies, organizations can streamline operations and prepare to tackle the complexities of modern supply chain management. The time to act is now; investing in freight data analytics will lead to a more efficient and resilient logistics future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is freight data analytics?
Freight data analytics involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data related to freight transportation, including shipment volumes, routes, carriers, and delivery times.
Why is understanding freight data analytics important for logistics professionals?
Understanding freight data analytics is crucial for logistics professionals as it helps enhance their operations by allowing them to leverage information more effectively, improving efficiency and refining decision-making processes.
What are the key components of freight analytics?
The key components of freight analytics include data sources, data categories, and analytical techniques.
What are the data sources in freight analytics?
Data sources in freight analytics include transportation management systems (TMS), warehouse management systems (WMS), and external data feeds.
What types of data categories are recognized in freight analytics?
The recognized data categories in freight analytics include historical shipment records, real-time tracking details, and predictive analysis.
What analytical techniques are important in freight data analytics?
Important analytical techniques in freight data analytics include descriptive analysis (what happened), diagnostic analysis (why it happened), and predictive analysis (what is likely to occur).




