Introduction
The logistics industry is experiencing a significant shift as businesses pursue innovative solutions to improve efficiency and accuracy. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) emerges as a crucial tool that not only streamlines operations but also promotes real-time collaboration throughout the supply chain. As organizations face the challenge of maintaining speed and precision in a rapidly changing environment, a critical question arises: how can mastering EDI transform logistics operations and lead to substantial enhancements in both performance and sustainability?
Define EDI and Its Importance in Logistics
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) represents the electronic exchange of business documents between organizations in a standardized format. In logistics, the use of EDI for logistics facilitates the seamless exchange of information, including purchase requests, invoices, and shipping notifications, eliminating the need for paper-based communication. The significance of EDI for logistics is profound as it streamlines operations, reduces errors, and accelerates transaction speeds. By automating data exchange, EDI minimizes manual entry, which is often susceptible to mistakes, thereby enhancing overall accuracy and efficiency in supply chain management.
The advantages of EDI are underscored by its ability to improve transaction accuracy through automation, covering the entire process from procurement to payment. This results in a reduction of transaction errors by 30-40%. For instance, EDI enables quicker handling at speeds that are 40% faster than manual methods, a crucial factor in today's fast-paced logistics environment where timely and precise deliveries are paramount.
Real-world examples further demonstrate EDI's impact on supply chain efficiency. A logistics firm utilizing EDI for transaction management has experienced a significant reduction in lead times, allowing for just-in-time (JIT) inventory methods that lower storage costs. Moreover, EDI supports real-time data exchange, granting businesses immediate access to critical information, which enhances inventory control and boosts customer satisfaction.
As noted by Whimsy Intermodal, "From real-time request handling to automated billing and paperless transactions, our EDI-enabled operations guarantee that we provide exceptional service while aiding a more sustainable planet." The use of EDI for logistics operations not only optimizes workflows but also promotes sustainability by reducing paper usage and minimizing the environmental footprint. In summary, EDI for logistics is an essential tool in modern supply chains, driving efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability.

Explore EDI Applications in Supply Chain Management
EDI plays a pivotal role in optimizing supply chain management through various applications:
-
Order Processing: Automating the exchange of purchase orders and confirmations significantly accelerates the order fulfillment process. This automation shortens handling times and improves the accuracy of requests, resulting in greater customer satisfaction. Companies can achieve substantial reductions in order processing times by implementing EDI for logistics, with some reporting improvements of up to 58% in transaction efficiency.
-
Inventory Management: EDI provides real-time data updates that enable precise inventory tracking and management. This capability minimizes the risks of stockouts and overstock situations, allowing companies to maintain optimal inventory levels and reduce warehousing costs. Additionally, the environmental benefits of EDI for logistics, such as reduced paper usage, contribute to cost savings and operational efficiency.
-
Shipping Notifications: EDI for logistics streamlines the exchange of shipping notices and tracking information, which enhances visibility throughout the supply chain. This transparency enables companies to proactively manage logistics and respond to potential delays.
-
Invoicing: Automated invoicing through EDI decreases handling times and minimizes errors, ensuring timely payments and enhanced cash flow. This efficiency is crucial for maintaining healthy financial operations.
-
Collaboration: EDI fosters enhanced collaboration between trading partners by standardizing communication protocols. This standardization leads to stronger relationships and improved service levels, ultimately benefiting all parties involved. The automation of request handling and inventory control using EDI for logistics not only enhances operations but also positions companies competitively in the evolving digital landscape.
Looking ahead, future trends in EDI include advancements in cloud-based EDI and AI-powered data analytics, which are expected to further enhance supply chain management.

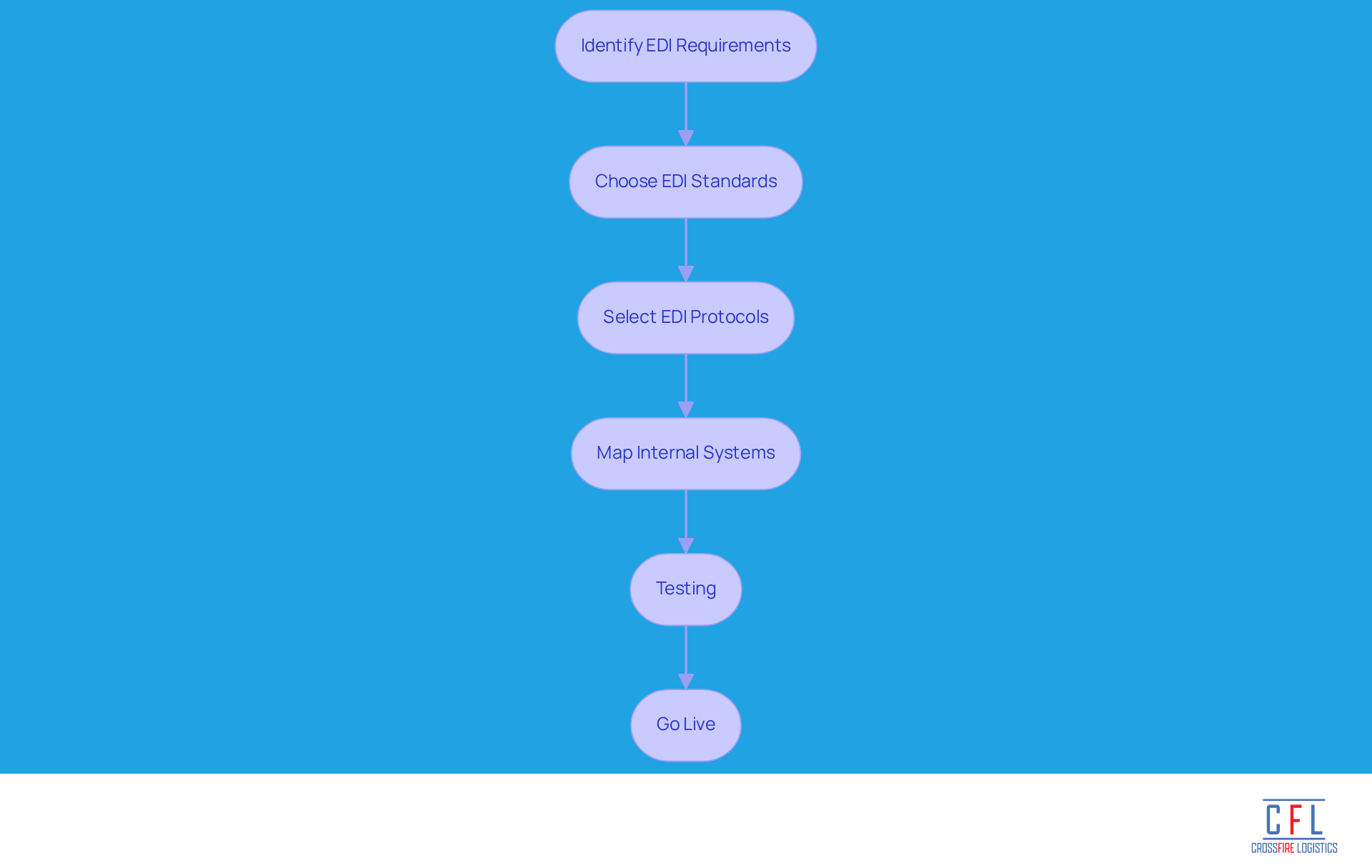
Implement EDI: Standards, Protocols, and Setup Steps
To implement EDI effectively, organizations must follow several key steps:
-
Identify EDI Requirements: Evaluate your organizational needs and determine which documents will be exchanged electronically. This foundational step helps pinpoint inefficiencies in current processes, such as slow order processing or shipment tracking.
-
Choose EDI Standards: Common standards include ANSI X12 and EDIFACT. Selecting the right standard is crucial for compatibility with trading partners, as different industries may have specific requirements. For instance, healthcare often uses HL7, while automotive sectors may prefer ODETTE.
-
Select EDI Protocols: Protocols such as AS2, FTP, or HTTP are used to transmit EDI documents securely. AS2 is particularly favored for its security and widespread adoption among large buyers, while FTP offers simplicity for smaller operations. Selecting a protocol that matches your organizational needs is crucial for effective communication.
-
Map Internal Systems: Ensure that your internal systems (ERP, WMS) can integrate with EDI. This may involve mapping data fields to ensure compatibility, similar to creating a blueprint for data flow between your organization and trading partners.
-
Testing: Conduct thorough testing with trading partners to ensure that documents are exchanged correctly and that systems communicate effectively. This phase is critical for identifying and resolving potential issues before going live.
-
Go Live: Once testing is successful, implement EDI in your daily operations. Continuous monitoring for issues and optimizing processes as necessary will help maintain efficiency and reliability.
By adhering to these steps, companies can greatly improve their operational efficiency, decrease turnaround times from days to minutes, and enhance overall data precision in their supply chain management through the use of EDI for logistics. As noted, "The key to a seamless EDI implementation lies in understanding that there's no one-size-fits-all solution." Additionally, regular evaluations and updates are necessary to keep the EDI system functioning optimally, ensuring that organizations can adapt to changing business needs.
Identify Benefits of EDI Integration for Logistics Efficiency
The integration of EDI for logistics into operations offers numerous benefits, particularly for companies like Crossfire Logistics, which provides comprehensive warehousing and drayage services in Hampton Roads. These benefits include:
- Increased Efficiency: EDI automates routine tasks, significantly reducing the time spent on manual data entry and processing, which is crucial for Crossfire Logistics' operations.
- Cost Savings: By minimizing paper usage and administrative costs, EDI for logistics can effectively lower operational expenses, aligning with Crossfire Logistics' commitment to on-time and on-budget solutions.
- Improved Accuracy: The use of EDI for logistics reduces human error, leading to more accurate order processing and inventory management, which is essential for maintaining the high standards of service that Crossfire Logistics is known for.
- Faster Transaction Times: The use of EDI for logistics enables near-instantaneous communication between trading partners, speeding up the overall transaction cycle, which is vital for efficient supply chain management.
- Enhanced Visibility: The use of EDI for logistics facilitates real-time data exchange, providing better visibility into inventory levels and shipment statuses, allowing for more informed decision-making, a key aspect of Crossfire Logistics' strategic partnerships.
- Stronger Relationships: EDI for logistics fosters better collaboration and communication with trading partners, which leads to improved service levels and customer satisfaction, thereby reinforcing Crossfire Logistics' reputation for award-winning customer service.

Conclusion
Mastering Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is crucial for logistics organizations aiming to boost operational efficiency and accuracy. By adopting EDI, businesses can automate the exchange of essential documents, which significantly reduces manual errors and transaction times. This shift not only streamlines logistics operations but also promotes real-time collaboration, enabling companies to respond quickly to market demands and customer expectations.
The article outlines several key benefits of EDI, such as:
- Improved transaction accuracy
- Faster order processing
- Better inventory management
Specific applications, including automated invoicing and shipping notifications, further demonstrate how EDI enhances supply chain management. The implementation steps provided offer a clear roadmap for organizations seeking to integrate EDI effectively, ensuring compatibility with trading partners and internal systems.
Ultimately, embracing EDI in logistics transcends a mere technological upgrade; it signifies a strategic move towards sustainability and enhanced service delivery. Companies are encouraged to explore the numerous benefits of EDI integration, from cost savings to improved visibility, and to take proactive measures in mastering this essential tool. By doing so, organizations can position themselves competitively in the dynamic logistics landscape, ensuring they meet the demands of a fast-paced market while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the electronic exchange of business documents between organizations in a standardized format.
Why is EDI important in logistics?
EDI is important in logistics because it facilitates the seamless exchange of information, such as purchase requests, invoices, and shipping notifications, while eliminating the need for paper-based communication.
How does EDI improve logistics operations?
EDI improves logistics operations by streamlining processes, reducing errors, and accelerating transaction speeds, which enhances overall accuracy and efficiency in supply chain management.
What are the advantages of using EDI in logistics?
The advantages of using EDI in logistics include improved transaction accuracy through automation, a reduction of transaction errors by 30-40%, and quicker handling speeds that are 40% faster than manual methods.
How does EDI impact lead times and inventory management?
EDI helps reduce lead times, allowing for just-in-time (JIT) inventory methods that lower storage costs. It also supports real-time data exchange, enhancing inventory control and customer satisfaction.
What role does EDI play in sustainability?
EDI promotes sustainability by reducing paper usage and minimizing the environmental footprint of logistics operations, contributing to more eco-friendly business practices.
Can you provide an example of EDI's impact on logistics?
A logistics firm utilizing EDI for transaction management has experienced significant reductions in lead times, enabling them to implement just-in-time inventory methods and improve overall service efficiency.




