Introduction
The logistics landscape is evolving. Businesses are increasingly seeking innovative solutions to meet the demands of a fast-paced market. At the forefront of this transformation are transloading warehouses. These facilities facilitate the swift transfer of goods between different transportation modes, offering unparalleled flexibility and efficiency.
However, traditional warehousing remains a staple for many companies. It provides stability and structured inventory management. As these two approaches vie for dominance in supply chain strategies, a critical question arises: which method truly delivers the best value? Under what circumstances should each be employed?
Define Transloading and Traditional Warehousing
Transloading warehouse represents a logistics process that involves transferring goods between different modes of transportation during shipment. This often includes temporary storage and repackaging within a transloading warehouse, which enhances flexibility and allows for efficient movement. For instance, goods can be transferred from shipping containers to trucks for final delivery. In contrast, traditional warehousing is primarily focused on the long-term storage of goods within dedicated facilities. This method emphasizes structured stock management, where items are retained until they are needed for distribution. Typically, traditional warehouses are utilized for bulk items that require stable inventory levels and predictable demand.
Recent trends in 2025 reveal a growing preference for cargo transfer, largely due to its speed-to-market advantages. This is particularly significant for industries like fashion retail, where responsiveness to trends is essential. Logistics specialists note that freight transfer can lead to considerable cost reductions, with typical direct savings ranging from $1,500 to $4,300 per container. Additionally, it enhances delivery durations, making it a more appealing option compared to conventional storage methods. For example, fashion retailers employing cross-docking can respond to trends over 30 days faster than those relying on traditional storage solutions.
Key differences between these approaches lie in their operational focus. Intermodal transfer prioritizes quick transfers and flexibility, while conventional storage emphasizes stability and long-term solutions. As companies increasingly seek flexibility within their supply chains, the role of cargo transfer at the transloading warehouse continues to grow, posing challenges to traditional warehousing practices. Furthermore, the environmental benefits of cargo transfer, such as reduced carbon footprints and improved sustainability, are becoming increasingly relevant to logistics coordinators who aim to enhance their corporate social responsibility initiatives.

Compare Operational Processes of Transloading and Traditional Warehousing
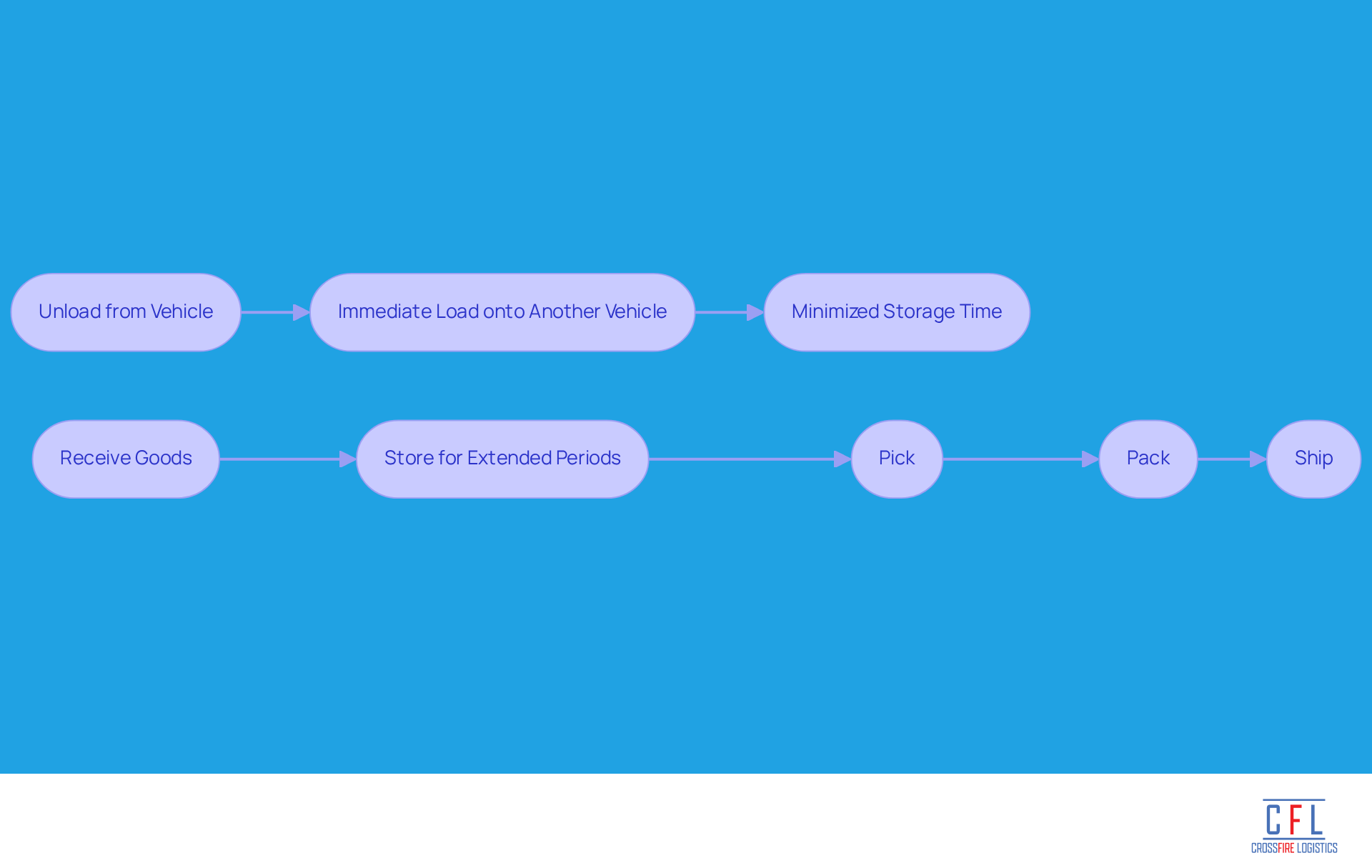
Transloading is defined by its operational efficiency, characterized by rapid transfers between different transportation modes. In this process, goods are unloaded from one vehicle and immediately loaded onto another, which significantly minimizes storage time. This requires precise coordination and often involves using a transloading warehouse for temporary storage to effectively manage the flow of goods.
In contrast, traditional warehousing follows a more structured approach. Goods are received, stored for extended periods, picked, packed, and then shipped. While this method allows for detailed inventory management, it can result in longer lead times and higher holding costs due to the prolonged storage of goods.
Evaluate Pros and Cons of Transloading vs. Traditional Warehousing
Transloading offers several advantages, including significant reductions in transportation costs, enhanced flexibility in shipping routes, and expedited turnaround times due to decreased storage durations. For instance, companies utilizing cross-docking can save an average of $2,500 per container. Some clients have reported delivery time reductions from three weeks to just 12 days without any price increases. One agricultural client remarked, "Your team turned our three-week delivery into 12 days - without price hikes."
However, transloading also presents challenges. It can lead to increased handling costs and the risk of damage during cargo transfers, particularly for fragile items. Industry studies reveal that 30% of global shipping delays stem from inefficient cargo transfers, resulting in additional costs for businesses.
In contrast, conventional warehousing provides stability and improved control over stock management, making it suitable for businesses with predictable demand patterns. This model often incurs higher holding costs, with total conventional warehouse expenses ranging from $1,950 to $5,100 per container, plus outbound freight. Furthermore, longer lead times associated with inventory turnover can lead to inefficiencies, as goods may spend up to 40% more time in transit compared to transloaded shipments. Typical storage expenses for conventional facilities can vary from $200 to $500 per container each month, underscoring the financial implications of this model.
Ultimately, the choice between a transloading warehouse and conventional storage hinges on a company's specific logistics requirements and operational objectives. While a transloading warehouse can optimize costs and enhance delivery speed, it necessitates careful management to mitigate risks related to handling and potential damage. Conversely, conventional warehousing provides a reliable framework for stock management but may not be as cost-effective or adaptable to market fluctuations. Additionally, sustainability practices, such as reducing carbon emissions through efficient logistics, are increasingly vital in modern supply chain considerations.

Identify Suitable Scenarios for Transloading and Traditional Warehousing
A transloading warehouse offers significant advantages for businesses that require the swift movement of goods across various transportation modes. This makes it an ideal choice for international shipping operations or companies facing container shortages. Industries experiencing fluctuating demand or those aiming to optimize their distribution routes particularly benefit from this approach. For instance, high-volume brands often utilize cross-docking to enhance speed and adaptability, allowing for quick stock changes in response to real-time demand. Crossfire Logistics complements this with fulfillment and cross-docking services, providing a comprehensive solution for businesses looking to streamline their logistics operations.
Conversely, conventional storage is best suited for businesses with consistent stock needs, such as retailers or producers with predictable sales trends. This method excels in offering long-term storage solutions for companies that can manage stock over extended periods. For example, manufacturers with regular production schedules can effectively use conventional storage methods to maintain a steady supply of raw materials and finished products, ensuring operational efficiency. Crossfire Logistics' storage services are tailored to assist these companies, enabling substantial cost reductions and improved stock management.
In conclusion, the choice between a transloading warehouse and conventional storage hinges on the specific logistical needs of a business. Companies should evaluate factors such as inventory stability, demand variability, and transportation efficiency when determining the most suitable warehousing strategy. By assessing their unique circumstances and operational goals, businesses can make informed decisions. Crossfire Logistics is well-equipped to assist in this evaluation with its comprehensive solutions.

Conclusion
The comparison between transloading warehouses and traditional warehousing underscores the evolving landscape of logistics, where flexibility and speed increasingly take precedence over long-term storage solutions. Transloading represents a dynamic approach that facilitates the rapid movement of goods across various transportation modes, catering to businesses that require agility in their supply chain operations. In contrast, traditional warehousing emphasizes stability and structured inventory management, making it suitable for companies with predictable demand.
Key insights reveal that transloading can significantly reduce costs and enhance delivery times, particularly for industries needing to respond quickly to market changes. While transloading offers benefits such as lower transportation expenses and faster turnaround times, it also presents challenges, including potential handling costs and the risk of damage during transfers. Conversely, traditional warehousing provides a reliable framework for stock management, though it may incur higher holding costs and longer lead times.
Ultimately, the decision between utilizing a transloading warehouse or traditional warehousing should be guided by the specific logistics needs and operational objectives of a business. Companies must assess their inventory stability, demand variability, and transportation efficiency to determine the most effective warehousing strategy. Embracing the appropriate logistics solution not only optimizes costs but also enhances responsiveness to market dynamics, highlighting the importance of strategic decision-making in supply chain management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is transloading in logistics?
Transloading is a logistics process that involves transferring goods between different modes of transportation during shipment, often including temporary storage and repackaging within a transloading warehouse.
How does transloading enhance flexibility in shipping?
Transloading allows for efficient movement of goods, enabling transfers from shipping containers to trucks for final delivery, which increases responsiveness and speed in logistics.
What is the main focus of traditional warehousing?
Traditional warehousing primarily focuses on the long-term storage of goods within dedicated facilities, emphasizing structured stock management for items that require stable inventory levels and predictable demand.
What are the recent trends in cargo transfer as of 2025?
There is a growing preference for cargo transfer due to its speed-to-market advantages, particularly in industries like fashion retail, where quick responsiveness to trends is crucial.
How much can companies save by using freight transfer?
Companies can experience direct savings ranging from $1,500 to $4,300 per container when utilizing freight transfer compared to traditional storage methods.
How does transloading impact delivery durations?
Transloading enhances delivery durations, allowing companies, especially in fashion retail, to respond to trends over 30 days faster than those relying on traditional storage solutions.
What are the key differences between transloading and traditional warehousing?
The key differences lie in their operational focus: transloading prioritizes quick transfers and flexibility, while traditional warehousing emphasizes stability and long-term solutions.
What environmental benefits does cargo transfer offer?
Cargo transfer can lead to reduced carbon footprints and improved sustainability, which are increasingly relevant to logistics coordinators aiming to enhance corporate social responsibility initiatives.




